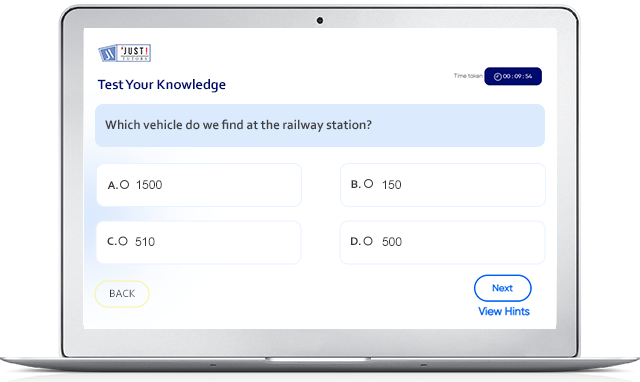

Attempt Free ICSE Class 6 Maths Exam MCQ Mock Test
Solving MCQ Questions for ICSE Class 6 With Answers on Just Tutors is the best way to revise and prepare for Examination.
MCQ Questions for ICSE Class 6 Maths With Answers
"JustTutors" brings you topic wise MCQ Questions for ICSE Class 6 Maths with all the subtopics from every chapter to test your knowledge. Multiple Choice Questions for ICSE Class 6 are available for free, you can test your knowledge anytime and share the links with your friends to help them check their knowledge.
In case you feel that your child needs assistance to get better in the lesson and needs support from the expert for the same, feel free to contact our expert tutors for FREE! Just visit Just Tutors and book a free demo session with a lass 6 Math teacher. The session will be interactive and you can learn with your comfort.

Topic Wise
MCQ Test
Answer questions based on every single topic

Exam
Simulation
Attempt exclusive test papers designed by expert faculty

In-Depth
Performance Analysis
Unlimited quizzes, mock tests & PDF notes
Incredible feedback from our students
Access to the best teachers, start your personalised learning journey for ICSE Class 6 Maths
Prepare yourself for ICSE Class 6 Maths
Enroll in upcoming courses that best suit your schedule and ICSE Class 6 Maths exam syllabus
At JustTutors, we believe in the power of digital technology to help students get personalized learning and attention from India's best-in-class science, english and math tutors. We are focused on creating a top-class e-learning platform that brings together the best teachers, technology, media, content for creating a seamless and world-class experience for every student.